Recent projects
GNETWORKS: Google matrix analysis of real complex networks
|


|
APEX: Analyse Physique des résEaux compleXes

 Grant from Région Bourgogne-Franche-Comté
Grant from Région Bourgogne-Franche-Comté
Project period: September 2017 - August 2020
Budget: 185k€
Website of APEX project
Project period: September 2017 - August 2020
Budget: 185k€
ApliGoogle: Application of Google matrix to directed networks and Big Data

 Nodes of the network
Nodes of the network
- Toulouse (UPS-CNRS) Klaus Frahm
and Dima Shepelyansky (network coordinator)
- Toulouse (INP-IRIT) Katia Jaffres-Runser (node leader)
- Besançon (UTINAM CNRS) José Lages (node leader)
- Paris (Institut Curie) Andrei Zinovyev (node leader)
Full description of the project
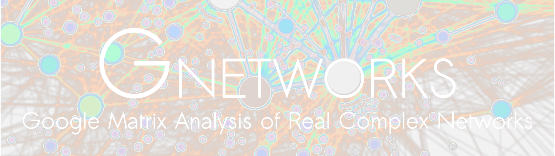
Project summary The huge amount of communications produced in our modern societies can be seen as a rich flux of data/metadata propagating through huge directed complex networks. The study of these networks becomes of primary importance particularly to analyze and to understand human knowledge, world trade, systems biology, and mobile telecommunications. In this interdisciplinary project we apply to Big Data (Wikipedia, World Trade Organization databases, omic networks, mobile telecommunications networks, ...) advanced analytic tools coming from theoretical physics and mathematics (Markov chains, Perron-Frobenius operators, Google matrix, Random Matrix Theory, quantum chaos, spectral matrix methods, ...).
WRWU: Wikipedia Ranking of World Universities
 Ongoing project since February, 1st 2015
Ongoing project since February, 1st 2015
Participants: José Lages, Antoine Patt, Dima Shepelyansky
First release of the ranking November, 29th 2015
Complete ranking lists, article, and supporting information
Worldwide media coverage
General audience presentation
April 1st, 2016, Workshop Magazine L'Etudiant.
Participants: José Lages, Antoine Patt, Dima Shepelyansky
First release of the ranking November, 29th 2015
Complete ranking lists, article, and supporting information
Worldwide media coverage
General audience presentation
April 1st, 2016, Workshop Magazine L'Etudiant.
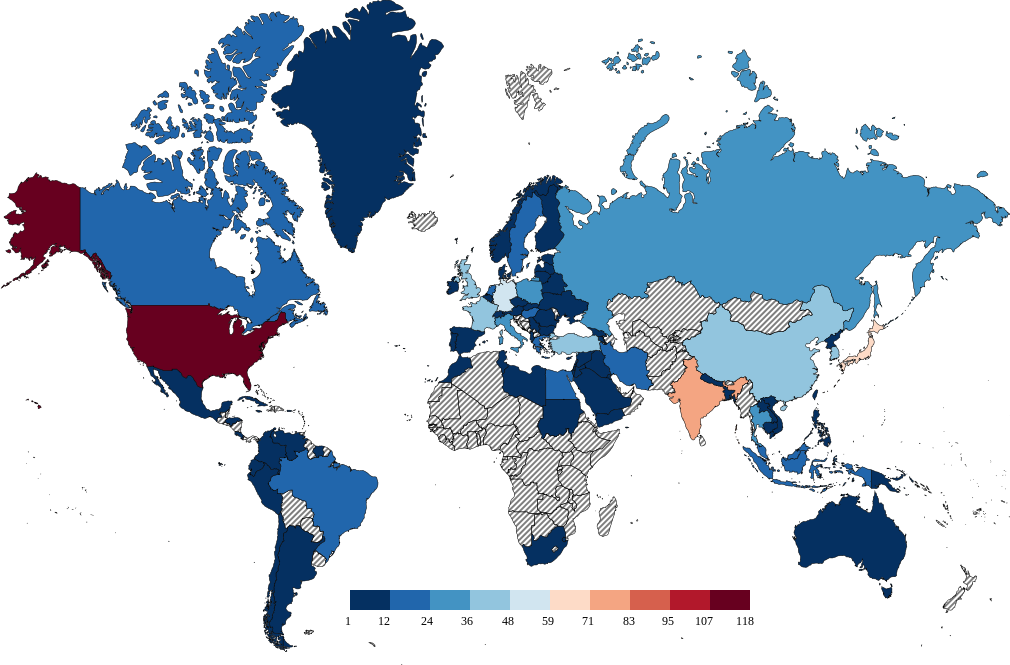
Project summary We use the directed networks between articles of 24 Wikipedia language editions for producing the wikipedia ranking of world Universities (WRWU) using PageRank, 2DRank and CheiRank algorithms. This approach allows to incorporate various cultural views on world universities using the mathematical statistical analysis independent of cultural preferences.
Symplectic maps, Solar system dynamics and dynamics of exoplanets
 Grant from Région Bourgogne-Franche-Comté and SRO 2016 OSU THETA
Grant from Région Bourgogne-Franche-Comté and SRO 2016 OSU THETA
Project period: February-December 2016
Budget: 14.5k€ (11.5k€ Région BFC + 3k€ SRO OSU)
Articles
[22]
[25]
[26]
[27]
[27,html]
Project period: February-December 2016
Budget: 14.5k€ (11.5k€ Région BFC + 3k€ SRO OSU)
Articles [22] [25] [26] [27] [27,html]
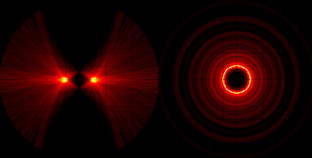
Project summary The project aims at a development of the theory of symplectic maps in application to problems of dynamics of Solar-system bodies and dynamics of exoplanets. The analytical study will be concentrated on the theory of generalized separatrix maps, known as the Kepler maps. The astronomical objects of interest for this project comprise comets, binary asteroids, circumbinary exoplanets, hyper-velocity stars.
Chaotic dynamics of (dark) matter in binaries
 Grant from SRO 2014 OSU THETA
Grant from SRO 2014 OSU THETA
Project period: February-December 2014
Budget: 4k€
Articles
[20]
[21]
[21, supporting video]
Media: France bleue Besançon émission EurÍka (in French)
General audience presentation
December, 18th 2014, Journée OSU THETA 2014
Project period: February-December 2014
Budget: 4k€
Articles [20] [21] [21, supporting video]
Media: France bleue Besançon émission EurÍka (in French)
General audience presentation
December, 18th 2014, Journée OSU THETA 2014
Main achievements
- We have shown a huge enhancement of dark matter density in binary systems. Dark matter density in the vicinity of a binary can be about 4000 more important than galactic dark matter density. The rotation velocity of the binary is responsible of this enhancement which is all the more important if binary rotation velocity is important.
- We constructed a two dimensional symplectic map to described 1P/Halley chaotic dynamics isolating the energy transfer to comet coming from the 8 Solar system planets.
Chaotic dark matter in the Solar System
 Grant from SRO 2012 OSU THETA
Grant from SRO 2012 OSU THETA
Project period: February-December 2012
Budget: 2k€
Articles
[18]
Media: CNRS hebdo, délégation centre-est
Project period: February-December 2012
Budget: 2k€
Articles [18]
Media: CNRS hebdo, délégation centre-est
Main achievements We computed the dark matter mass captured by the Solar System. The chaotic capture mechanism is induced by the 3-body interaction between the Sun, Jupiter and dark matter particles passing through the Solar System.